HEC-SS
Company Profile
Hongkong Electric Power Investment Co., Ltd. (Hongkong Electric-SS) is one of the oldest power companies in the world. Its Hongkong Electric Co., Ltd. (Hong Kong Electric) was established in 1889 and launched its business activities in 1890. This includes power generation, transmission, distribution and power supply services to Hong Kong Island, Ap Lei Chau and Lamma Island.
The main power generation facility of HEC is the Lamma Island Power Station. The power generation fuel used in the power station includes natural gas, coal, wind and solar energy. The entire power generation, transmission and distribution process is controlled by a fully computerized system control center. Hourly monitoring, keeping the power supply highly reliable with advanced technology.
HEC-SS is the first fixed single investment letter in Hong Kong with power supply as its main business. It was spun off from the parent company Power Industry Co., Ltd. in 2014 and listed on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange on January 29, 2014.
Because the listing method adopted by HEC-SS is a joint listing, it is legally bundled by the shares of commercial trusts and listed companies, that is, holding a stock of a listed stock represents the holding of commercial trusts and listed companies respectively. Stocks, so the management of the stapled securities is the same as its listed company. This type of company's listing name will be followed by "SS" (Stapled Securities) for identification. In terms of overall business operations, stapled securities are generally the same as ordinary companies.
development path
Hong Kong Electric Light Co., Ltd. (Hong Kong Electric) was incorporated on January 24, 1889 and began supplying power to Hong Kong Island in December 1890. The HEC initially supplied electricity to parts of Hong Kong Island, including electric street lights in the Central Business District. The first power plant is the Wanchai Power Plant, located at Star Street, Wanchai, with an initial capacity of 100 kilowatts.
In 1922, the HEC began supplying electricity to the trams that were travelling in the northern part of Hong Kong Island.
In 1968, HEC built a fully computerized power plant in Ap Lei Chau and used fuel to generate electricity. The power plant was completed in 1981 with a power generation of 1,061 megawatts.
In September 1978, the Hong Kong Government officially approved the construction of a larger power plant at Lamma Island by the HEC. The construction of the power plant was planned in three phases.
In 1981, the HEC was acquired by Hong Kong Land Holdings Limited.
In 1983, Hong Kong’s future was unresolved, and interest rates were high. At that time, Hong Kong Land Holdings Co., Ltd., which was heavily in debt, sold the HEC at a low price to Hutchison Whampoa, which is owned by Li Ka-shing.
In 1984, the first phase of the Nantun Power Plant was completed, including three 250 MW coal-fired generating units and ancillary facilities, as well as the entire power plant used to treat and store fuel and coal.
In December 1989, the Ap Lei Chau Power Plant officially ceased operation.
In 1991, the second phase of the Nantun Power Plant was completed, including three 350 MW generator sets with a semi-outdoor coal-fired boiler, a 55 MW gas turbine and six 125 MW gas turbines.
In 1997, the third phase of the Nantun Power Plant was completed. The third phase of the project included two 350 MW coal-fired generating units. In July of the same year, the HEC System Control Center was officially opened. The system control center is located in the Ap Lei Chau Electric Light Building and monitors the entire power supply system 24 hours a day.
In 2006, in support of renewable energy development and environmental protection, HEC built Hong Kong's first wind power station (Nanfeng Wind Power Station) in Daling, Lamma Island, with 800 kW wind turbines. In the same year, the expansion project of Nanxun Power Plant was developed on the reclamation land south of the power plant, and a total of six natural gas-fired combined cycle units could be built. The first 335 MW gas unit was connected to the grid in July 2006, using LNG from Australia, gasified by a natural gas receiving station in Shenzhen, and transported to the plant through a 92-kilometre submarine gas pipeline.
In July 2010, in order to use more renewable energy, Nanxun Power Plant launched a 550 kW solar power system and expanded to 1 MW in March 2013, increasing the total installed capacity of the power plant to 3,737 MW.
In 2013, HEC was integrated into HEC Power Investment Co., Ltd. (Hongkong Electric-SS).
On January 6, 2014, Li Ka-shing's power industry split the Hongkong Electric-SS listing proposal was approved by more than 99% of shareholders.
On January 29, 2014, HEC-SS was officially listed on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange.
Profit model
The main business of HEC-SS is to produce electricity and supply electricity to Hong Kong Island, Ap Lei Chau Island and Lamma Island. The business scope is limited to Hong Kong. The profit model is single and concentrated, but the competition is stable. As shown in the figure, electricity sales accounted for 99.76% of the operating income of the HEC-SS, while electricity-related income (wind energy, solar power subsidies, etc.) accounted for 0.24%.
As a power supply company, the price of electricity and electricity directly affects the company's income and profit levels. But in fact, because the HEC-SS has a profit control agreement with the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region Government (that is, the fee and price adjustment mechanism agreement between the Hong Kong Government and the public utilities), before 2008, the HEC-SS agreement The permitted profit is 13.5% per year. The profit control agreement can be called a "profit guarantee agreement". The Hong Kong people have complained about this. However, in the new profit control agreement effective from January 1, 2009, the Hong Kong SAR government lowered the permitted profit return rate of public utilities to 9.99%. The new agreement will last for ten years. After the expiration, the government may choose to continue the agreement. The period is five years. The Control Plan Agreement also contains provisions to encourage emission reductions, improve energy efficiency, improve operational performance, improve service quality and promote the use of renewable energy. Under the current regulatory framework, the profit control scheme can effectively balance the interests of customers and shareholders: customers can obtain reliable and stable power supply at reasonable prices, and a clear mechanism and stable long-term regulatory framework can also guarantee The rights and interests of shareholders.
In terms of electricity prices, the HEC-SS was down for the second consecutive year. In 2017, the price per kWh was lowered to HK$1.104, a decrease of 17.2% from HK$1.334 in 2016.
In terms of electricity sales, in 2014, HEC-SS sold 10.955 billion kWh, sold 10.87 billion kWh in 2015, and sold 10.792 billion kWh in 2016. It has been declining for three consecutive years, mainly because the Hong Kong government has vigorously promoted energy conservation and low carbon. The concept of an environmentally friendly life, so even if the number of registered users of the HEC-SS is increasing year by year, the sales volume is decreasing year by year.
Industry overview
Hong Kong's domestic power supply pattern is unlikely to change
There are actually only two of the most well-known power companies in Hong Kong - HEC and China Light and Power Co., Ltd. (CLP). The former mainly supplies electricity to Hong Kong Island, Ap Lei Chau and Lamma Island. The latter mainly supplies electricity to Kowloon and the New Territories. The local power supply in Hong Kong is actually monopolized by the "two powers".
Although the Hong Kong Government does not have a specific threshold for the new power company, interested investors can enter the Hong Kong electricity market as long as they meet the requirements on power supply reliability, safety and environmental performance. However, given the land use requirements for the construction of new generator sets, it is not easy for new competitors to find suitable places. In addition, the small size of Hong Kong's domestic market requires huge capital investment and no new investors for many years. Incoming.
Future public utility new control plan agreement will further reduce the permitted rate of return
Both HEC and CLP have entered into a profit control agreement with the Hong Kong Government. The permitted return rate under the agreement is 9.99% of the average net fixed assets. Before the last adjustment, the permitted rate of return was as high as 13.5% of the average net fixed assets. The regulatory agreement between the Hong Kong Government and the HEC will expire on December 31, 2018, and the regulatory agreement with CLP will expire on September 30, 2018. However, in 2017, the Hong Kong Government and the HEC and CLP have entered into a new profit control scheme agreement. The new Hongkong Electric Control Scheme Agreement will run from January 1, 2019 to December 31, 2033, for a period of 15 years. And CLP's new profit control plan for more than 15 years, from October 1, 2018 to December 31, 2033. In the new scheme agreement entered into between the two power companies and the Hong Kong Government, the permitted profit level was set at 8% of the average net value of its fixed assets.
Hong Kong Government plans to develop more renewable energy in the future
For a long time, the Hong Kong Government has been promoting Hong Kong to become a low-carbon, livable, intelligent and sustainable city. For the power industry, it is also required to ensure that all operations and facilities of the power company comply with the government's environmental regulations. At the same time, it is necessary to minimize the environmental impacts of production operations, such as energy conservation and emission reduction, thereby protecting and improving the environment. Maintain close liaison and cooperation with the Environmental Protection Agency and the Environmental Protection Department to create a better environment.
Renewable energy is in line with the "zero emission" principle. However, due to the lack of suitable land for the construction of power generation facilities in Hong Kong, development in this area has been restricted. Despite this, HEC is still actively studying how to use more renewable energy. In fact, in addition to setting up Hong Kong's largest solar power system and wind power station on Lamma Island, HEC also proposed the construction of an offshore wind farm with a capacity of 100 MW. According to the feasibility study data, the proposed wind farm can produce enough green energy for 50,000 families. At present, HEC is working closely with relevant companies to find the solution that best suits the people of Hong Kong.
Financial overview
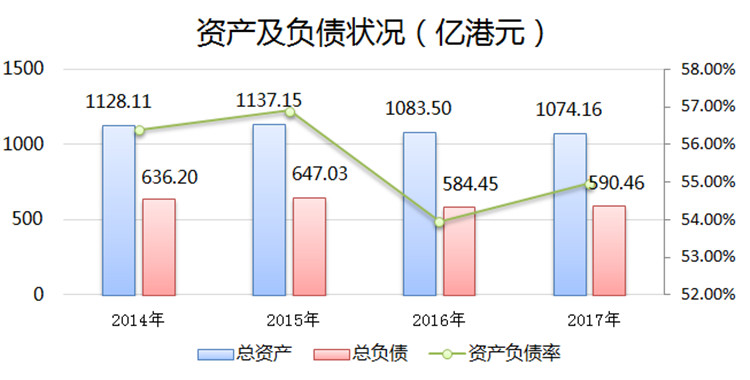
According to the 2016 annual report, HEC-SS revenue was HK$11.21 billion, up 6.7% year-on-year; net profit was HK$3.591 billion, up 12.2%; available for distribution of revenue was HK$3.538 billion, equivalent to 2015; final dividends were paid per share order 20.12 HK cents, together with a dividend of 19.92 HK cents for the interim period, contributed a total dividend of 40.04 HK cents for the year, also equivalent to 2015; net profit attributable to shareholders increased by 0.2% from 2015 to HK$3.599 billion; electricity sales compared to 2015 108.79 billion degrees fell by 0.7% to 10.792 billion kWh, mainly due to the Hong Kong government's vigorous promotion of energy conservation, environmental protection, low-carbon life and the relatively weak retail industry in Hong Kong.
In the first half of 2017, the interim results showed that HEC-SS revenue was HK$5.326 billion; net profit was HK$1.03 billion, down 8.9% year-on-year; financial costs increased slightly; total liabilities were HK$40.4 billion, and asset-liability ratio was 54.97%. In addition, HEC-SS will invest HK$10 billion in capital expenditures for maintenance every five years. The capital expenditure for 2019-2023 is estimated to be at least HK$14.5 billion, but this will also contribute to the growth of net fixed assets. The hedged profit control scheme agreement was partially affected by a 9.99% reduction to 8%.
Advantages and prospects
As a local power supply company in Hong Kong, the advantages of HEC-SS are as follows:
1. Have a strong customer base to provide customers with stable power generation, transmission, distribution and power supply services.
2. Have mature local brands and long-term relationships with customers, and business needs are stable.
3. Power supply reliability and operational performance are widely recognized.
For investors, the HEC-SS maintains a stable and substantial dividend, which is a good investment target for defensive investors.
Risk and crisis
1. The power supply range is limited to Hong Kong Island, Ap Lei Chau Island and Lamma Island.
2. After the implementation of the new profit control scheme agreement on January 1, 2019, the permitted profit of HEC-SS will be reduced from the current 9.99% to 8%, thus affecting the company's profit level.
3. Electricity sales have declined in recent years.
company information
Company Name Hongkong Electric Power Investment Co., Ltd.
Time to market 2014-01-29
Official website https://www.hkelectric.com
management team
Chairman of the Board of Directors Huo Jianning
CEO Yin Zhitian
Chief Financial Officer Huang Jianwen
Listed exchange
Hong Kong Stock Exchange
Industry Utilities
Address 44, Kennedy Road, Hong Kong
Largest shareholder power industry co., ltd